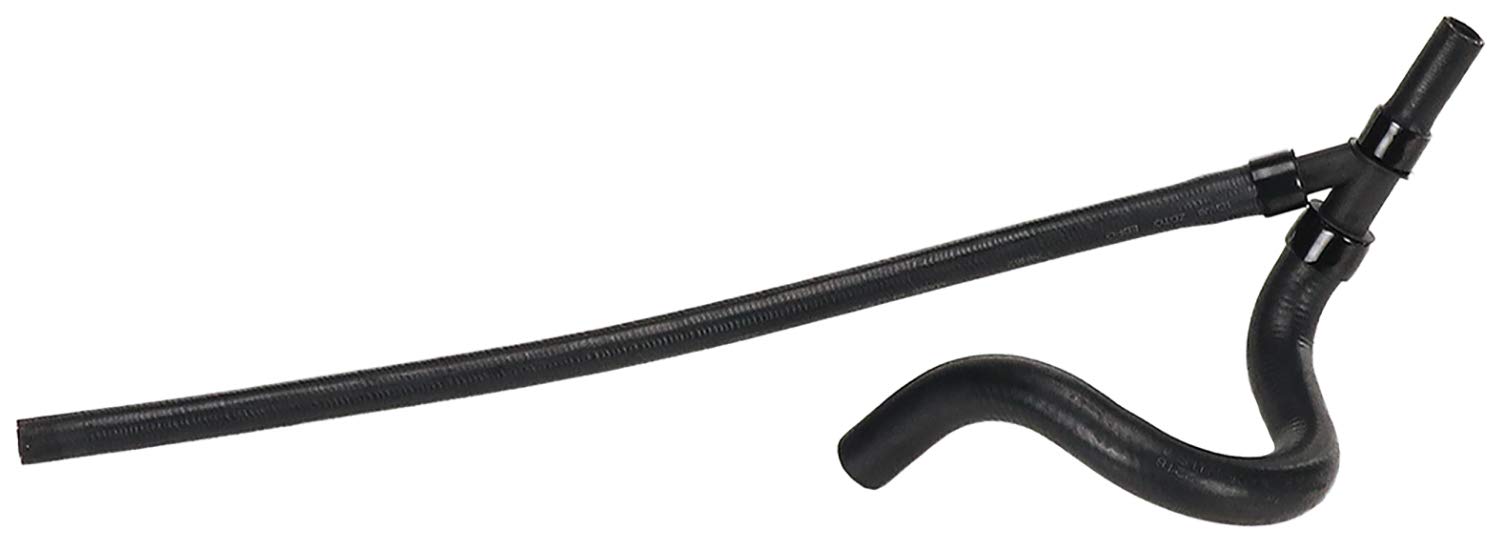
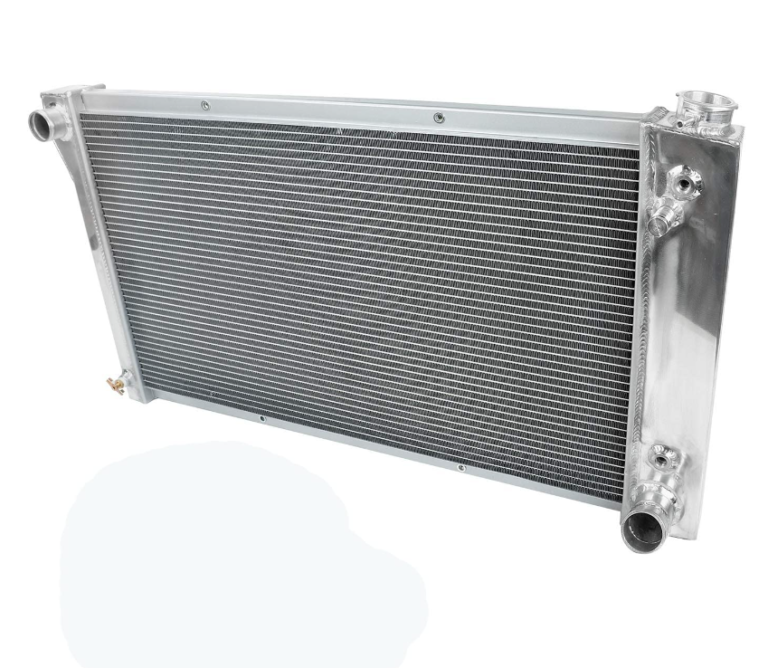
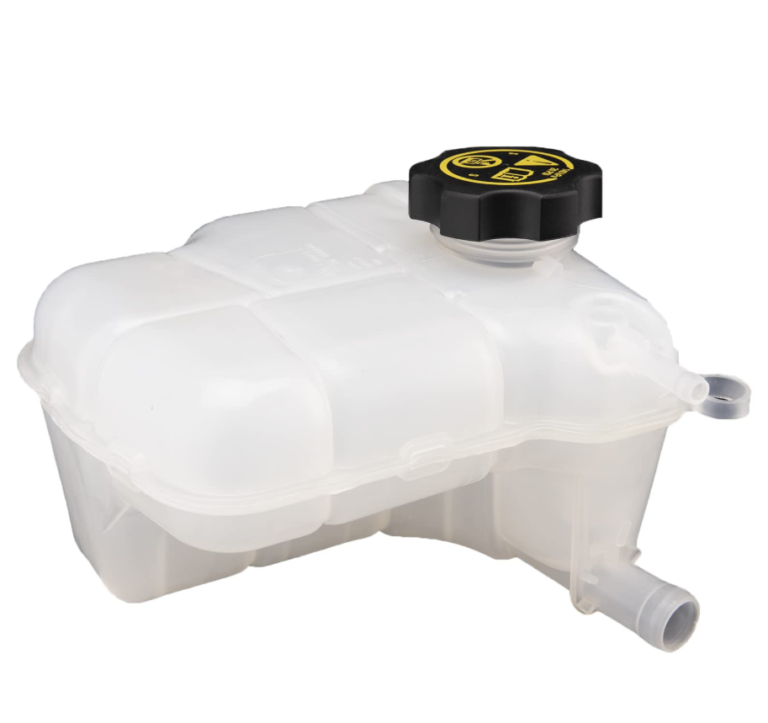
The radiator hose is an essential part of a car’s cooling system. It transports coolant between the engine and the radiator, as well as back to the engine, facilitating the regulation of the engine’s temperature. These hoses connect key components such as the engine, radiator, and expansion tank.
Functions of the Radiator Hose
- 1. Transporting Coolant:
- • The primary role of the radiator hose is to circulate coolant, ensuring the engine maintains an optimal operating temperature. The coolant absorbs heat from the engine, cools down in the radiator, and is then sent back to the engine through the hose for continuous circulation.
- 1. Maintaining System Pressure:
- • Radiator hoses assist in the movement of coolant while helping regulate system pressure via components like the radiator and expansion tank. Some hoses are equipped with pressure valves at connection points to help with pressure regulation.
- 1. Connecting Cooling System Components:
- • Radiator hoses link various parts of the cooling system. They are typically divided into the upper radiator hose (from the engine to the top of the radiator) and the lower radiator hose (from the radiator back to the engine). These hoses are usually made of rubber or other high-temperature-resistant materials.
- 1. Conducting Heat:
- • Radiator hoses not only transport coolant but also endure high temperatures and pressures. They must maintain stability under varying conditions, preventing coolant leaks or hose ruptures.
Common Types of Radiator Hoses
- • Upper Radiator Hose: Connects the engine or water pump to the top of the radiator and typically carries hot coolant from the engine.
- • Lower Radiator Hose: Connects the bottom of the radiator to the engine and usually transports cooled coolant back to the engine.
- • Bypass Hose: Some vehicles have additional hoses that allow coolant to flow between the engine, radiator, and expansion tank as needed.
Materials
Radiator hoses are typically made from high-temperature-resistant rubber or synthetic materials, such as silicone or polyurethane. These materials are chosen for their durability, resistance to heat, pressure, aging, corrosion, and wear.
Common Issues
- 1. Aging or Cracking:
- • Over time, radiator hoses may deteriorate due to exposure to high temperatures, chemical corrosion, or friction, leading to cracks or breaks. A ruptured hose can cause coolant leakage and result in engine overheating.
- 1. Leaks:
- • Hose connections may become loose or corroded, leading to coolant leaks. Insufficient coolant can compromise cooling efficiency and cause the engine to overheat.
- 1. Blockages or Damage:
- • Accumulated debris inside the hoses or physical damage can obstruct coolant flow, reducing the efficiency of the cooling system and risking engine overheating.
Maintenance and Inspection
- • Regularly check the radiator hoses for visible signs of wear, such as cracks, hardening, or abrasions.
- • Ensure the hose connections are secure and free of leaks.
- • Monitor coolant levels and inspect the hoses for proper coolant flow.
In conclusion, radiator hoses are indispensable to the functionality of a car’s cooling system, ensuring the consistent flow of coolant and preventing the engine from overheating. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn-out hoses are essential for maintaining a car’s optimal performance and longevity.